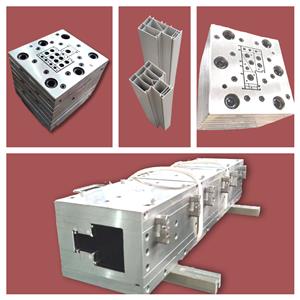
El plástico PVC, la construcción del molde de extrusión, revela el velo para usted
Hay dos formas de moldes comúnmente utilizados: moldes escalonados de placas y moldes de gradiente de sección transversal. La trayectoria del flujo del molde escalonado de placas cambia en pasos, y está formado por varias plantillas de boca conectadas en serie. Cada placa se mecaniza en una forma de contorno correspondiente, que cambia gradualmente desde la forma redonda de la entrada hasta la forma de salida deseada. Hay biseles en la entrada de cada bloque para completar la transición de una forma a otra. Este tipo de costo de procesamiento de moldes es bajo, el canal de flujo no tiene la optimización ideal y generalmente no es necesario utilizarlo como perfil principal. El corredor del molde con gradiente de sección es aerodinámico, no puede haber ninguna zona de retención del material en el corredor, la masa fundida se distribuye de manera gradual y precisa a cada sección de la forma de salida desde el círculo en la entrada, y la velocidad aumenta constantemente hasta el velocidad de salida requerida, y la velocidad de cada punto de la sección es la misma. Para perfiles de plástico PVC con núcleos de molde complejos, el núcleo del molde está integrado con la placa de soporte, algunos se fijan a la placa de soporte mediante pasadores y tornillos de ubicación y otros se incrustan en la placa de soporte mediante una incrustación apretada. No se puede desmontar fácilmente durante el uso porque lleva mucho tiempo volver a montarlo y depurarlo. La derivación de la masa fundida también se realiza de dos formas: en el cono de derivación y en la sección de compresión. El molde de gradiente de sección se puede utilizar como molde de perfil principal. El molde de extrusión de perfiles de plástico de PVC es la parte central de la línea de producción de extrusión, que incluye una matriz de boca (también conocida como cabezal de matriz), un molde de conformación, un tanque de agua de refrigeración, etc. La matriz de boca se ensambla con la brida en el cabezal del extrusor mediante de una brida, y el anillo calefactor, la placa calefactora, la fuente de alimentación y el termopar están conectados. El molde de conformación y el tanque de agua de refrigeración se fijan a la mesa de conformación con tornillos, y se conectan la tubería de agua y la tubería de gas. La estructura básica de la matriz de extrusión generalmente se diseña como una estructura de múltiples plantillas apiladas y ensambladas. Por lo tanto, el canal de flujo de todo el troquel se forma conectando uno de los canales de flujo en cada pieza de la plantilla, por delante y por detrás. La placa se coloca y se fija con pasadores y pernos para formar una matriz de extrusión monolítica. La situación básica es: la sección de flujo constante de la matriz de extrusión a menudo se compone de una placa perforada y la mitad frontal del cuello, y la mitad frontal y la segunda mitad del cuello también están diseñadas como dos plantillas, el cuello y la placa de transición del cuello. También es posible no utilizar una placa porosa, sino diseñar la mitad frontal del canal de flujo del cuello en un canal de flujo cilíndrico para estabilizar el flujo. La sección dividida del troquel de extrusión comienza desde la segunda mitad del cuello e incluye el cono dividido, la placa de soporte dividida y la placa retráctil. La placa retráctil no se puede dividir en un solo encofrado, sino junto con la placa preformada, en un encofrado. La sección de formación de la matriz de extrusión incluye las siguientes plantillas: placa de cavidad (también conocida como placa preformada), plantilla de boca (también conocida como placa de formación) y núcleo (también conocido como núcleo de molde). Para matrices de perfil más simples, la placa preformada se combina con la plantilla de boca en un encofrado. 1. Puntos clave del diseño de la sección transversal del producto El punto clave del diseño del producto de perfil de plástico PVC es que el espesor y la forma de cada sección deben distribuirse simétricamente, de modo que el flujo de material en el cabezal de la máquina esté equilibrado y el enfriamiento pueda ser uniforme. , y la presión tiende a estar equilibrada. En general, el espesor máximo de pared y el espesor mínimo de pared de una misma sección son diferentes < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1